News
From Pre-Charge to Full Power: The Five Stages of Safe Lithium Battery Charging
• Monitoring fever is a top priority.
• Lithium battery charging uses five stages to ensure safety: pre-charge, thermal control, constant current, constant voltage, and monitoring stop
1. The second line of protection - safety first
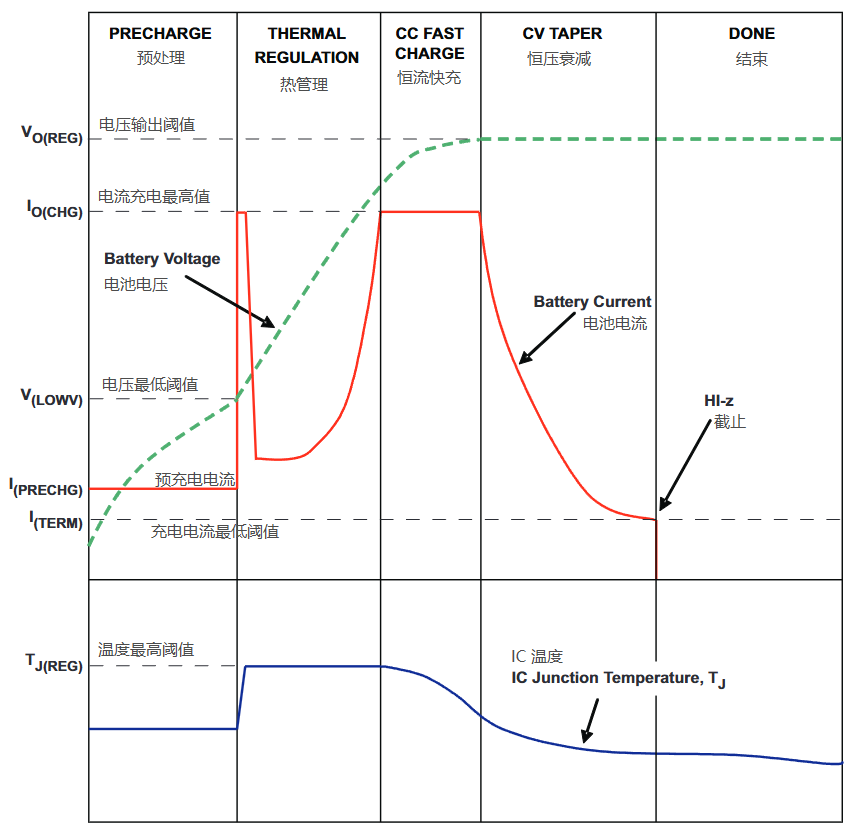
2. Preprocessing
Why does battery charging require a pre-processing stage?
Before explaining the situation , we must clarify an objective premise:
From the perspective of the charging management chip: there is a very low voltage (about 2.5V) at its battery port, which is not in the voltage range of a normal battery (3.2V~4.2V).
There are three situations at this time :
• It is not connected to a 4.2v single-cell lithium battery, but connected to something unknown.
• The connecting circuit or battery is damaged, and the voltage is abnormally low.
• (。・∀・)ノ゙Hey, this stupid battery is over-discharged~
But as a charging chip, he couldn't be sure, he could only try.
The charging chip will first try to apply a very small current (10% of the normal current or about 10mA). If a lithium battery is connected and the battery status is normal, the voltage at the battery end should slowly and continuously rise until it reaches the minimum battery charging voltage.
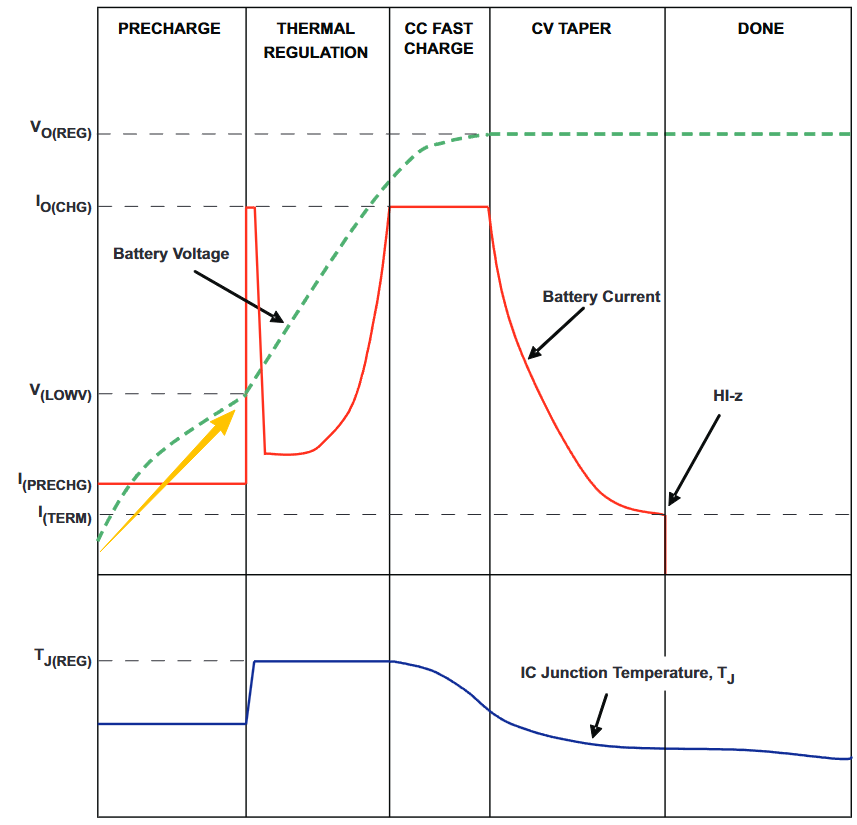
Why do we need to charge slowly during the pre-treatment charging stage?
A single-cell lithium-ion battery with extremely low power has a larger internal resistance

A resistor with normal charge

According to the power formula
P = I² × R
• P is the heating power
• I is the current flowing through the internal resistance
• R is the internal resistance
The charging chip knows this, of course.
Maintain extremely low current → maintain extremely low heat generation → ensure battery safety
This is also the reason why some mobile phones cannot be turned on after being turned off after not being used for a long time, or it takes two or three hours to charge and turn on!
Slowly, the battery terminal voltage increases to a stable voltage before moving on to the next step and starting normal charging.
3. Thermal Control
Once the battery voltage has risen to the normal range, the chip will attempt to charge at the set maximum current. According to the power formula, the initial heating is very fast and may reach very high temperatures very quickly.
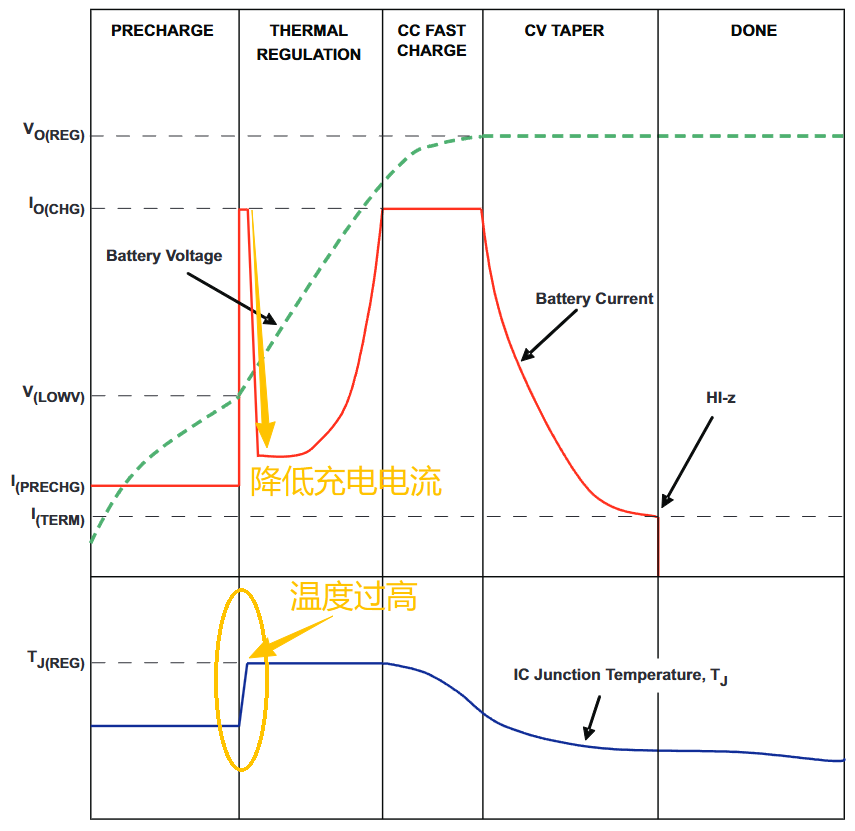
During this time, the charging chip will judge based on the battery temperature:
• Battery is overheating → Reduce charging current
• Battery temperature is normal → gradually increase the current value → reach the set current
As charging progresses, the internal resistance of the battery gradually decreases.
According to the power formula
P↓ = I² × R↓
The heating power is also decreasing, and the current can be safely increased slowly until the internal resistance is negligible.
4. Constant current boost
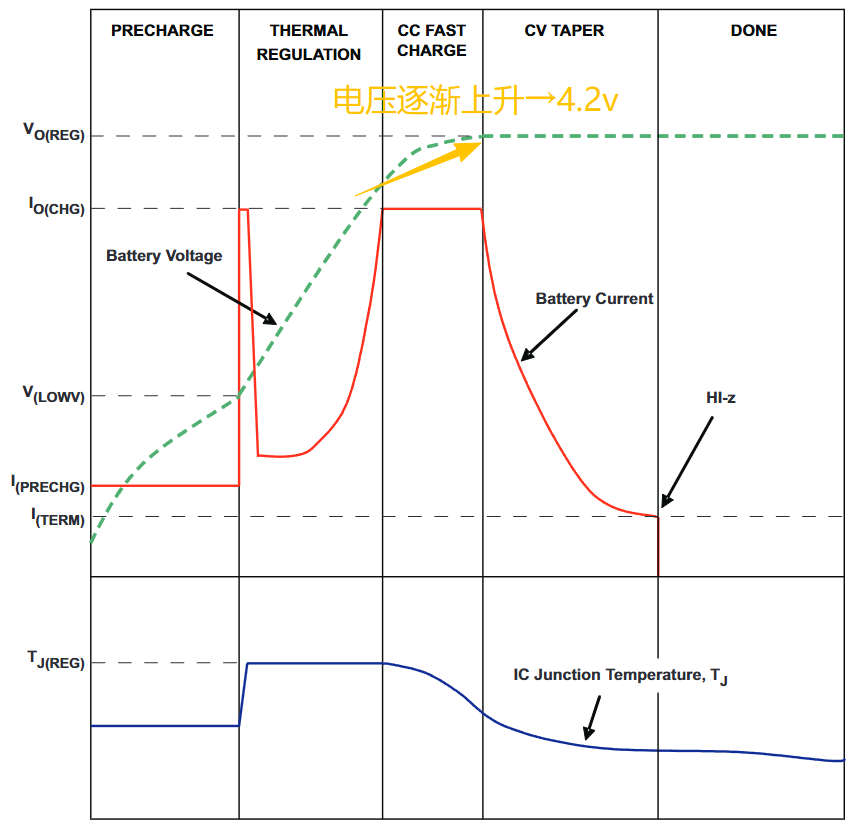
The lithium battery charging chip will charge according to the set maximum current value. At this time, the battery cell voltage will gradually rise until the battery voltage approaches 4.2v.
This stage will last for a long time until it reaches 4.2v and enters the next stage.
5. Constant pressure and current reduction
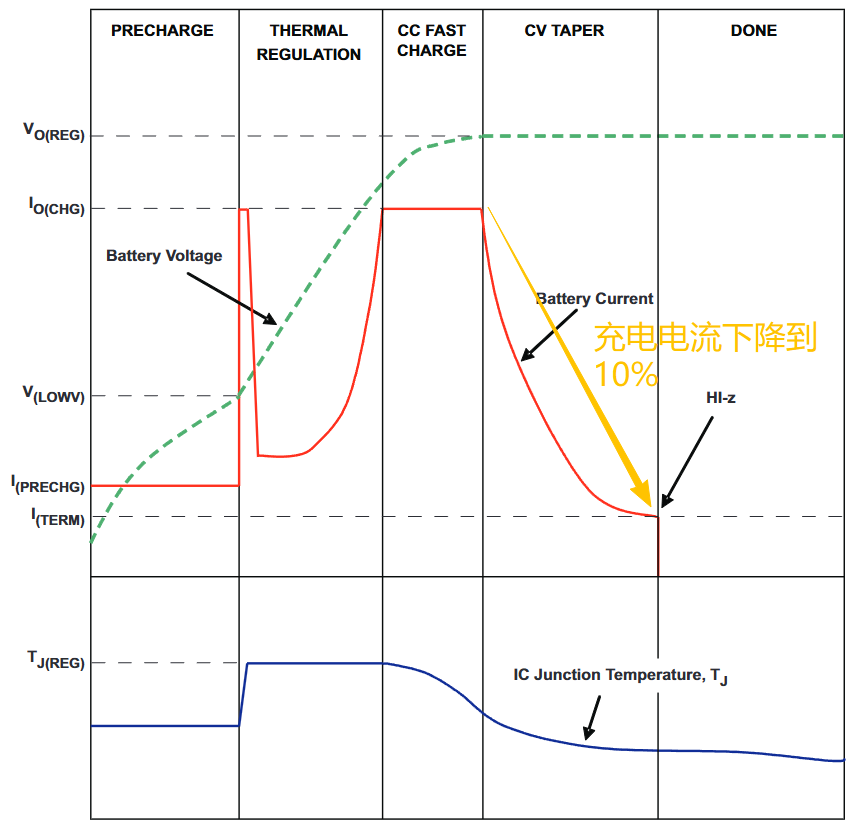
When the battery cell reaches 4.2V, the charging current will gradually decrease until it reaches 10%.
6. End charging
Finally, when the charging current drops to the cut-off current, stop charging. Do not stop when the charging current reaches 0! This means the battery is already overcharged. Deliberate undercharging is required to extend the battery life.


