News
The Complete Guide to Cylindrical Li-ion Batteries: Types, Performance, and Applications
Cylindrical lithium batteries are divided into different systems such as lithium iron phosphate, lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, cobalt-manganese hybrid, and ternary materials. The casing is divided into steel casing and polymer casing. Different material systems have different advantages.
Complete list of cylindrical lithium battery models
|
Cell model |
nominal voltage |
Capacity (mAh) |
Charging temperature (°C) |
Discharge temperature (°C) |
Charging current (A) |
Discharge current (A) |
|
ICR18650 (Ternary) |
3.7V |
2200 |
0~45 |
-40~+60 |
2.2A (room temperature 1C) |
10A (normal temperature 5C) |
|
ICR18650 (Ternary) |
3.7V |
2500 |
0~45 |
-40~+60 |
2.5A (room temperature 1C) |
25A (room temperature 10°C) |
|
ICR18650 (Ternary) |
3.7V |
3000 |
0~45 |
-40~+60 |
3.0A (normal temperature 1C) |
15A (5°C) |
|
ICR21700 (Ternary) |
3.7V |
4000 |
0~45 |
-40~+60 |
4.0A (normal temperature 1C) |
40A (normal temperature 10C) |
|
NCR18650B (Ternary) |
3.6V |
3350 |
0~45 |
-20~60 |
1.625A |
4.875A |
|
INR18650-30Q (Ternary) |
3.6V |
3000 |
0~45 |
-20~75 |
0.5C |
15A |
|
IFR26650 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) |
3.2V |
3200 |
-20~+45 |
-40~+60 |
3.2A (room temperature 1C) |
10A (room temperature 3C) |
|
IFR32700 (Lithium Iron Phosphate) |
3.2V |
5000 |
-20~+45 |
-40~+60 |
5.0A (normal temperature 1C) |
25A (5°C) |
|
IFR26650 E3400 |
3.2V |
3400 |
0~60 |
-10~60 |
2.0A |
10.2A |
I.What is a cylindrical lithium battery?
1. Definition of cylindrical battery
Cylindrical lithium batteries are classified into different systems, including lithium iron phosphate, lithium cobalt oxide, lithium manganese oxide, cobalt-manganese hybrid, and ternary materials. The casings are available in steel and polymer types, each with its own advantages. Currently, cylindrical lithium iron phosphate batteries with steel casings are the most common. These batteries offer advantages such as high capacity, high output voltage, good charge-discharge cycle performance, stable output voltage, high current discharge capability, stable electrochemical performance, safety, wide operating temperature range, and environmental friendliness. They are widely used in solar lighting, lawn lighting, backup power, power tools, and toy models.
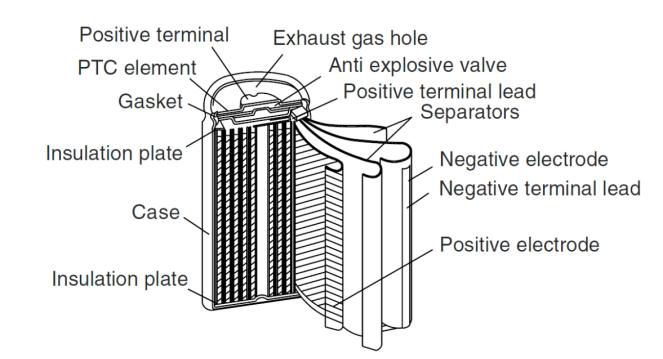
2. Cylindrical battery structure
A typical cylindrical battery structure includes: casing, cap, positive electrode, negative electrode, separator, electrolyte, PTC element, gasket, safety valve, etc. Generally, the battery casing is the negative electrode, and the cap is the positive electrode. The battery casing is made of nickel-plated steel.
3. Advantages of cylindrical lithium batteries
Compared to pouch and prismatic lithium batteries, cylindrical lithium batteries have the longest development history, a higher degree of standardization, more mature technology, higher yield rate, and lower cost.
Mature production process, low PACK cost, high battery product yield, and good heat dissipation performance.
Cylindrical batteries have established a series of internationally unified standard specifications and models, with mature technology suitable for mass continuous production. The cylindrical shape has a large specific surface area, resulting in good heat dissipation.
Cylindrical batteries are generally sealed batteries, and there are no maintenance issues during use.
The battery casing has high pressure resistance and will not exhibit phenomena such as swelling as seen in square or soft-pack batteries during use.
4. Cylindrical battery cathode material
Currently, the mainstream commercial cylindrical battery cathode materials mainly include lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2), lithium manganese oxide (LiMn2O4), ternary lithium (NMC), and lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4). Different material systems have different characteristics, as compared below:
|
project |
Lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂) |
Ternary lithium (LiNiCoMnO₂) |
Lithium manganese oxide (LiMn₂O₄) |
Lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄) |
|
Tap density (g/cm³) |
2.8~3.0 |
2.0~2.3 |
2.2~2.4 |
1.0~1.4 |
|
Specific surface area (m²/g) |
0.4~0.6 |
0.2~0.4 |
0.4~0.8 |
12~20 |
|
Capacity (mAh/g) |
135~140 |
140~180 |
90~100 |
130~140 |
|
Voltage plateau (V) |
3.7 |
3.5 |
3.8 |
3.2 |
|
Cyclic performance |
≥500 times |
≥500 times |
≥300 times |
≥2000 times |
|
Raw material costs |
High (cobalt content) |
High (containing nickel and cobalt) |
low |
low |
|
Environmental protection |
Contains cobalt (low environmental friendliness) |
Contains nickel and cobalt (China Environmental Protection) |
Non-toxic |
Non-toxic |
|
Safety performance |
Poor |
better |
good |
excellent |
|
Application areas |
Small batteries |
Small power battery |
Power batteries, low-cost batteries |
Power batteries/ultra-large capacity power supplies |
|
advantage |
Small and medium-sized batteries have stable performance |
Stable electrochemical performance |
Manganese resources are abundant and low in cost |
High safety and long lifespan |
|
shortcoming |
High cobalt price and low cycle life |
Cobalt and nickel are expensive |
Low energy density |
Poor low temperature performance |
5. Anode material for cylindrical batteries
Cylindrical battery anode materials can be roughly divided into six types: carbon anode materials, alloy anode materials, tin-based anode materials, lithium-containing transition metal nitride anode materials, nanoscale materials, and nano anode materials.
Carbon nanoscale anode materials: Currently, the anode materials actually used in lithium-ion batteries are basically carbon materials, such as artificial graphite, natural graphite, mesophase carbon microspheres, petroleum coke, carbon fiber, pyrolytic resin carbon, etc.
Alloy-based anode materials include tin-based alloys, silicon-based alloys, germanium-based alloys, aluminum-based alloys, antimony-based alloys, magnesium-based alloys, and other alloys. Currently, there are no commercially available products.
Tin-based anode materials: Tin-based anode materials can be divided into two types: tin oxides and tin-based composite oxides. Oxides refer to oxides of metallic tin in various valence states. Currently, there are no commercially available products.
There are currently no commercially available lithium transition metal nitride anode materials.
Nanoscale materials: carbon nanotubes, nanoalloy materials.
Nano-anode materials: Nano-oxide materials
II. Cylindrical Lithium Battery Cells
1. Cylindrical lithium-ion cell brands
Cylindrical lithium batteries are popular among lithium battery companies in Japan and South Korea, and there are also a considerable number of companies in China that produce cylindrical lithium batteries. The earliest cylindrical lithium battery was invented by Sony Corporation of Japan in 1992.
Well-known cylindrical lithium-ion battery cell brands include: Sony, Panasonic, Sanyo, Samsung, LG, Wanxiang A123, BAK, and Lishen.
2. Types of cylindrical lithium-ion cells
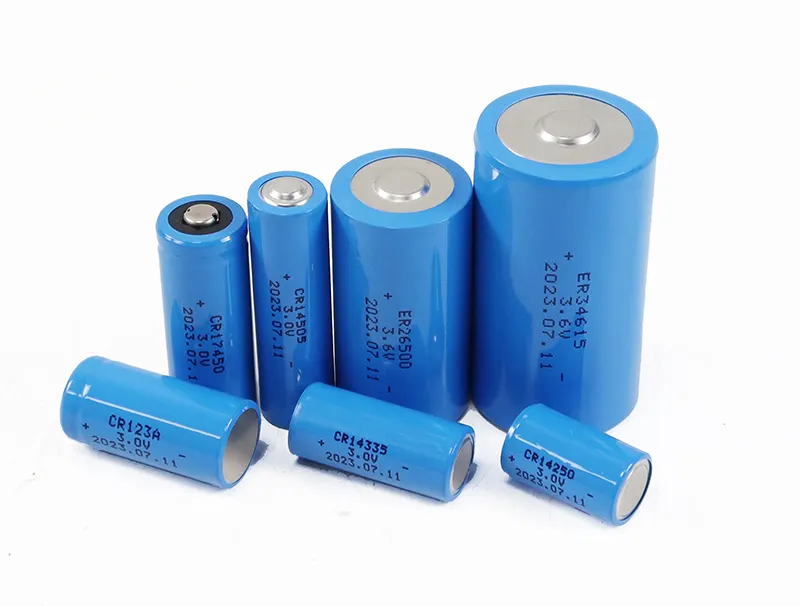
Cylindrical lithium-ion cells are typically represented by five digits. Counting from the left, the first two digits indicate the battery diameter, the third and fourth digits indicate the battery height, and the fifth digit indicates that the cell is circular. There are many models of cylindrical lithium batteries, with common ones including 10400, 14500, 16340, 18650, 21700, 26650, and 32650.
① 10440 Battery:
The 10440 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 10mm and a height of 44mm, the same size as what we commonly call a "size 7 battery". This type of battery generally has a very small capacity, only a few hundred mAh, and is mainly used in mini electronic products, such as flashlights, mini speakers, and megaphones.
② 14500 battery:
The 14500 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 14mm and a height of 50mm. This type of battery is generally 3.7V or 3.2V, with a relatively small nominal capacity, slightly larger than the 10440 battery, generally 1600mAh. It has excellent discharge performance and is mainly used in consumer electronics, such as wireless speakers, electric toys, and digital cameras.
③ 16340 battery.
The 16340 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 16mm and a height of 34mm. Because of its shorter height and relatively large capacity, this type of battery is frequently found in high-powered flashlights, LED flashlights, headlamps, laser lights, and other lighting fixtures.
④ 18650 Battery:
The 18650 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 18mm and a height of 65mm. Its biggest feature is its very high energy density, which is almost 170 Wh/kg. Therefore, this type of battery is a cost-effective battery. Most of the batteries we see in daily life are of this type because it is a relatively mature lithium battery with good system quality and stability in all aspects. It is widely used in battery capacity applications of around 10 kWh, such as in mobile phones, laptops and other small electronic devices.
⑤ 21700 Battery:
The 21700 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 21mm and a height of 70mm. Due to its increased size, the space utilization rate is improved, and the energy density of individual cells and the system can be increased. Its volumetric energy density is much higher than that of the 18650 battery. It is widely used in digital products, electric vehicles, balance vehicles, solar-powered lithium battery street lights, LED lights, power tools, etc.
⑥ 26650 Battery:
The 26650 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 26mm and a height of 65mm. It has a nominal voltage of 3.2V and a nominal capacity of 3200mAh. This type of battery has excellent capacity and high consistency, and has gradually become the replacement for 18650 batteries. Many products in the field of power batteries will also gradually favor this type.
⑦ 32650 Battery
The 32650 battery is a lithium battery with a diameter of 32mm and a height of 65mm. This type of battery has a strong continuous discharge capability, so it is more suitable for electric toys, backup power, UPS batteries, wind power generation systems, and wind-solar hybrid power generation systems.

III. Development of the Cylindrical Lithium Battery Market
Advances in cylindrical lithium-ion battery technology primarily stem from innovative research and application of key battery materials. The development of new materials further improves battery performance, enhances quality, reduces costs, and improves safety. To meet downstream applications' demands for higher battery specific energy, this is achieved through the use of materials with high specific capacity and by increasing charging voltage through the adoption of high-voltage materials.
Cylindrical lithium-ion batteries have evolved from the 14500 to the Tesla 21700 battery. In the near and medium term, while optimizing existing lithium-ion power battery technologies to meet the needs of large-scale development of new energy vehicles, the focus is on developing new lithium-ion power batteries, improving their safety, consistency, and lifespan, and simultaneously carrying out forward-looking research and development of new power battery systems.
For the medium- and long-term development of cylindrical lithium-ion batteries, while continuously optimizing and improving new lithium-ion power batteries, we will focus on developing new power battery systems to significantly improve specific energy, greatly reduce costs, and realize the practical application and large-scale application of new power battery systems.


